
以前很多新生婴儿都是父母自己照顾,但是现在人们的生活水平提高和生活状态也不一样了,对于宝宝的的健康成长越来受到重视了[详情]
压力扫描阀在汽车制造中的首要任务是对各个压力系统进行高精度的压力测试。它能够快速响应并准确调节至预设压力值
福州网站建设域名命名规范,网站域名怎么命名? 福州网站建设域名命名规范 不同后缀类别的网站域名很可能有不同的命名规范。为了获得成功的域名注册和根据网站域名的命名审批,您需 要遵循相应的网站域名命名规范。本文介绍了中文域名、英文域名,.hk对于其他域名的命名规范,您可以根据 项目需要掌握匹配标准,整体规划您的网站域名。

中央空调回收利用是符合国家的环保节能的理念的,因为现在有很多家庭都已经是安装了中央空调,而人们对于中央空调也是越来越喜爱,这种空调是需要有一定的保养方法的,也能够去延长使用的时间,那么这种类型的空调到底如何保养,要如何延长中央空调的使用时间呢,下面再为大家具体介绍一下。怎样延长中央空调的使用时间?
寰寰猫舍是WCF,TICA双认证专业猫舍,本猫舍猫咪性格温顺,血统纯正,自主繁育,售后系统完善,终身免费疫苗,欢迎爱猫人士选购!
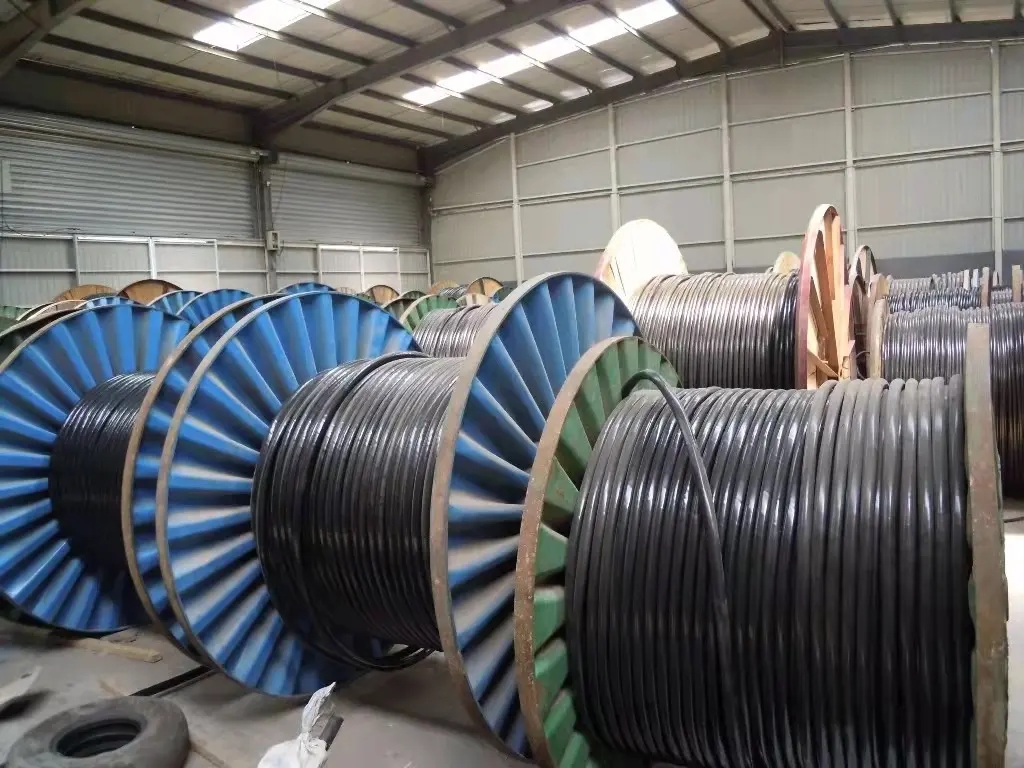

废旧电线电缆回收价格.河北物资回收公司再应用的作用是任何其余行业所无法代替的。 经济兴旺国度把物资回收再应用行业看作朝阳产业。随着我国经济的疾速开展,技巧的进步,更新换代的减速,会有越来越多的商品失去运用价值变成废旧商品,进入废旧商品回收再应用阶段。

母线槽在生产的时候使用价格低廉质量不过关的绝缘材料,切绝缘材料有针孔、厚薄不均匀,就会导致母线槽在使用中出现故障。在安装母线槽时有垃圾进入母线槽的壳体中,当这些垃圾在受潮时就会造成母线槽短路。 那遇到母线槽短路故障如何解决?

为了吸引更多的顾客和游客,网红夜市还设立了互动体验的主题商铺。这些商铺提供各种刺激和有趣的活动,同时也离不开灯光亮化设计的帮助。顾客们可以在这些商铺中玩得尽兴,享受到独特的购物体验,那么利用灯光亮化设计如何打造吸睛网红夜市?

EMC(电磁兼容性)滤波器是一种用于电磁干扰(EMI)的电子元件,广泛应用于各种电子设备中,以确保设备在其电磁环境中正常工作,同时不对其他设备造成干扰。EMC滤波器的主要功能是减少设备发出
乌鲁木齐清洗油烟机公司分享空调蒸发器的清洗方法 对于家电中清洗的步骤有很多,那么对于家用空调蒸发器是怎么样进行清洗的?乌鲁木齐清洗油烟机公司来为大家进行简单的分析一番。

铜仁西服定做讲讲西服根据制作方式严格来说分为三种,Bespoke(定制)、MTM(半定制) 和RTW(成衣)。Bespoke是的纯定制要求一件衣服上至少有五十个小时以上的手工活。而且量体打版、裁剪、制作都需要由一个人完成,非常依赖单个师傅的手艺,定做下来一趟价格价格不菲。

在校园中,旗杆的高度不仅关系到视觉效果,还关乎校园文化的传达与氛围的营造。因此,合理选择旗杆的高度是一个值得深入思考的问题。以下从几个方面分析校园旗杆的合适高度。
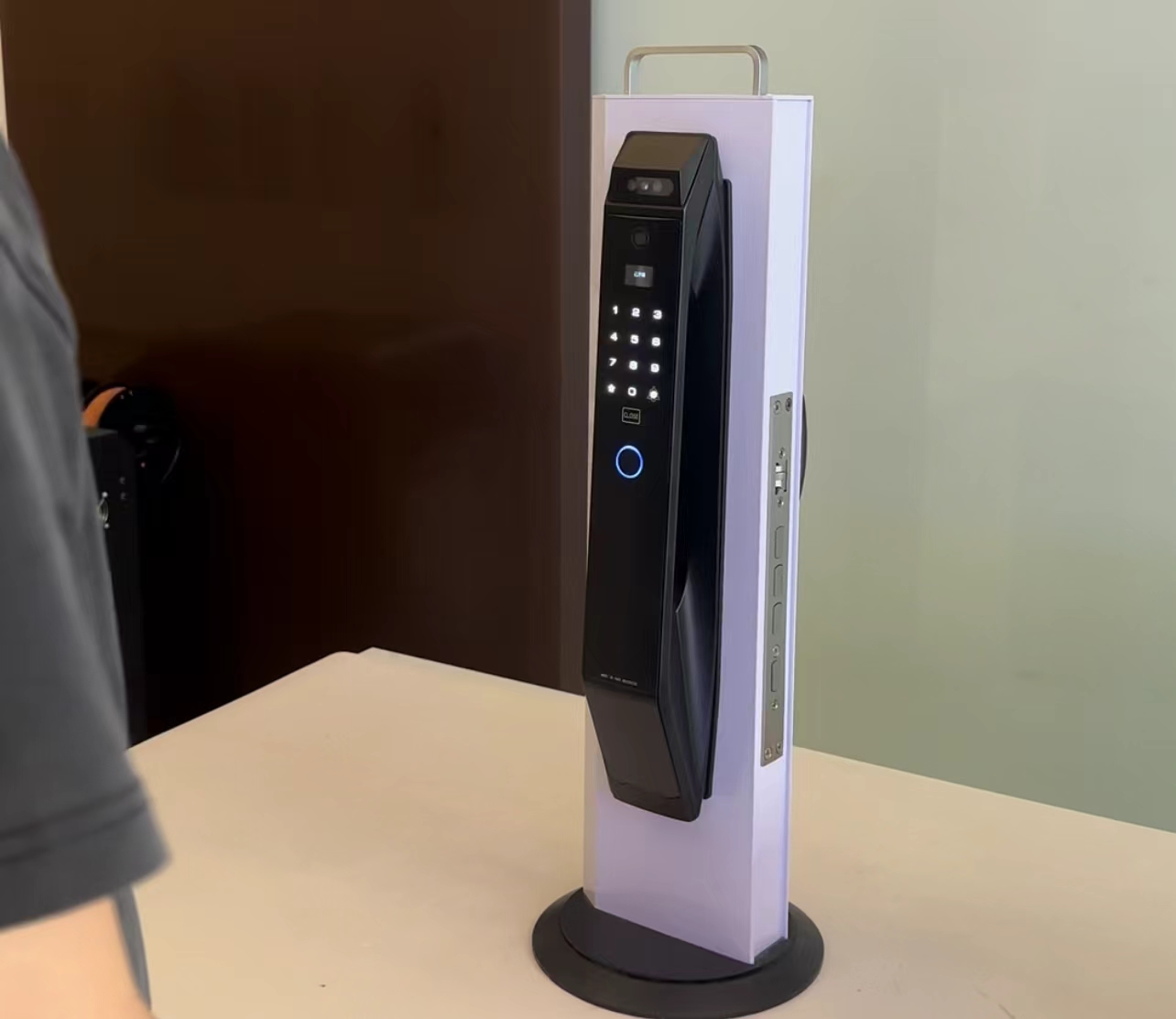

买智能锁最怕的是什么?是本想买台贵点的,希望它能质量好点、售后好点;但现实中,太多的事与愿违,结果却是更加的糟心。事实上我们也同样不想抛开品质和服务谈价格,这样既欺骗客户也欺骗自己。所以我们把最新上市的3D人脸识别款率先承诺“三年换新”,给选择它的客户一个安心的定心丸。

不干胶印刷如何安装色序?彩色不干胶印刷产品有满版实地,又有文字、线条、图案。印刷的色序首先印文字、线条、图案,然后再把满版实地放在上机印刷,这样可以避免由于不干胶纸厚,印迹未干时纸张相互碰撞擦坏、背面粘脏的现象。

车牌识别设备(LPR,License Plate Recognition)在现代交通管理和监控中发挥着重要作用,为了确保其正常运行和准确识别,正确的调试是必不可少的。以下是车牌识别设备调试的基本规定与步骤。

在雷雨天气中,防雷击的措施至关重要,尤其是在建筑物、工厂、通信设备和其他关键设施中。有效的防雷工程可以显著降低雷电对人身安全和财产损失的威胁。以下是关于防雷接地工程及其在雷雨天防雷击的详细讨论。

随着科技的不断进步,各类研究活动日益增多,实验室作为科研活动的重要场所,其设计合理与否直接影响到科研效率及成果的质量。本项目旨在设计一个现代化的科研实验室工程,以满足多学科、多领域的研究需求,提升科研人员的工作体验和效率。
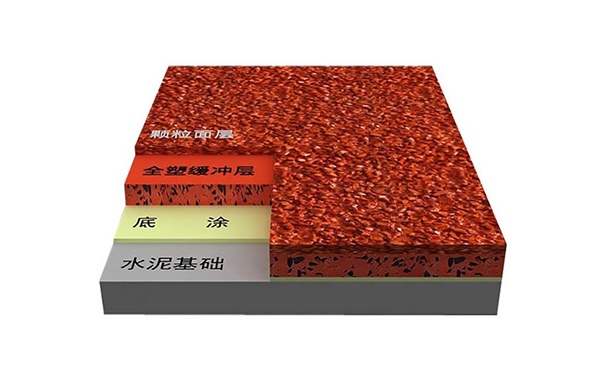
贵州塑胶跑道讲讲学校和体育馆都在使用户外塑胶跑道。户外塑胶跑道的优势高安全性可以防止摔倒造成的运动损伤,还可以适度吸收脚步的冲击,减少运动损伤,适合长期训练和比赛。
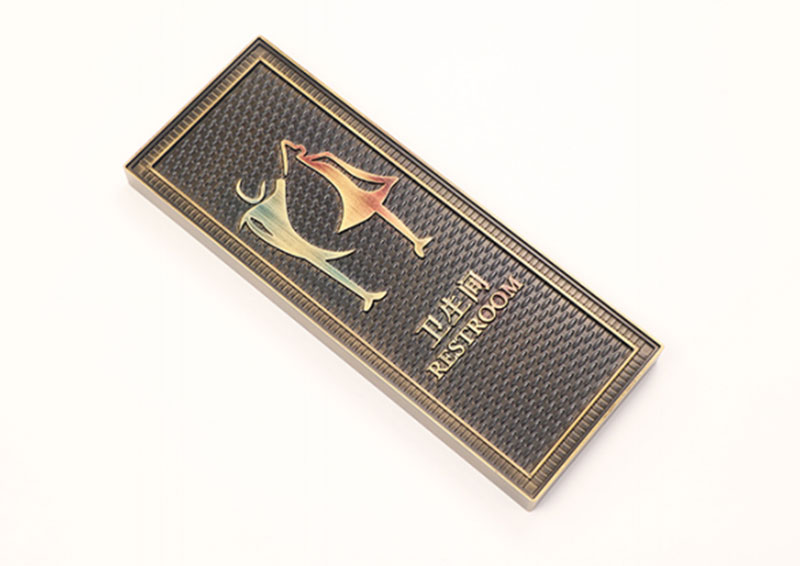

酒店标识牌以金属、木质材料为主,但工艺流程相对医院、校园、机关、写字楼标识的制作材料来说较为凌乱,运用的材料也比较多,多注重实用性与观赏性的结合。一般有户外的钢板镂空发光的精神堡垒,大堂内亚克力发光标识,大堂背景板的金属背光精工标识,大堂导视吊楣牌,公示牌,楼层分布牌,电梯牌,楼层牌,消防疏散牌,门牌等等,具体制作材料因不同要求而选取。

福州LED观片灯是一种用于医学影像诊断的设备,主要用于观察和分析X光片、CT片、MRI片等医学影像。其内部结构设计需要考虑光源、散热、控制电路、光学系统和外壳等多个方面。以下是LED观片灯的内部结构设计的详细描述。

小叶紫檀生长缓慢、质地坚硬,硬度为木材之首,系称“帝王之木”,非一般木材所能比。开料后有檀香味,呈橘红色,氧化后变为深褐色,最后变为紫色;纹理细密,变幻多样。凹凸传奇带你了解“帝王之木”印度小叶紫檀:
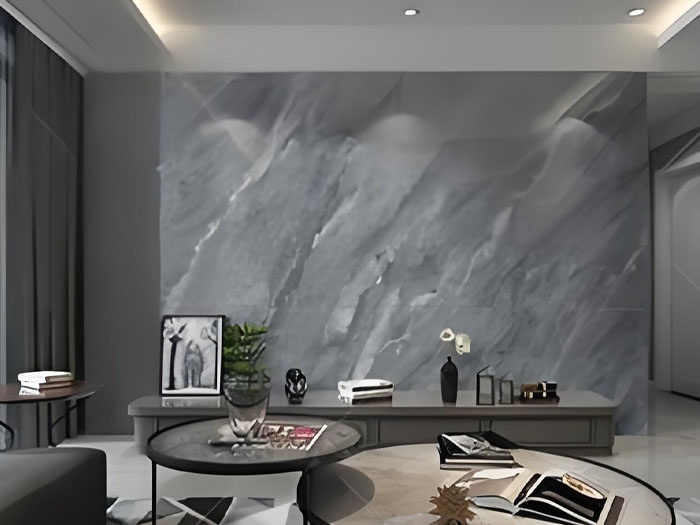

岩板边角易破损怎么办?云南岩板加工厂可对边角进行倒角 + 包边处理,用专用树脂胶加固,增强抗冲击性。运输前,在边角套上定制泡沫护角,并用胶带固定;堆放时,边角避免与硬物接触,底部垫木架隔离。

船舶定位导航与接收机的搭配使用是现代航运中不可或缺的技术,尤其是在复杂的海上环境中。定位导航系统能够确保船舶在海洋中航行时,准确掌握自己的位置、航向、速度等信息,从而保障航行安全。

清污机安装复杂吗?清污机安装的复杂程度,要看设备的类型和型号。小型家用清污机,结构相对简单,安装步骤少,通常按照说明书就能进行安装,新手也能轻松完成。比如,连接好刷头、插上电源,简单调试后就能使用。
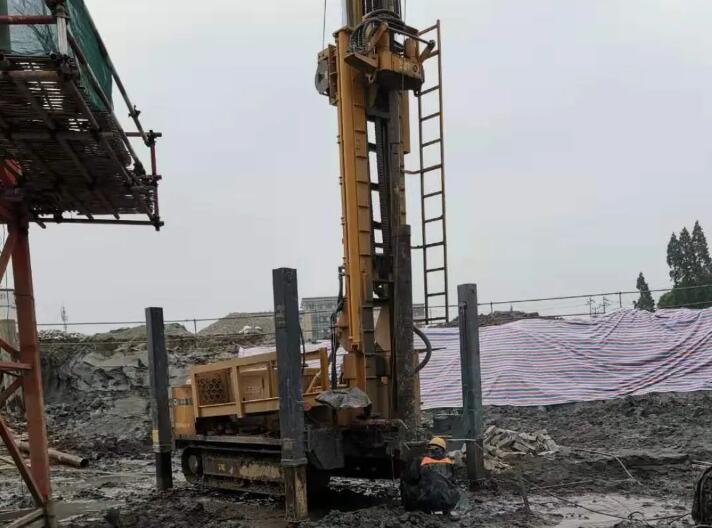

在降水打井作业中,安全始终是重中之重。特别是在城市或郊区,地下电缆纵横交错,稍有不慎就可能造成电缆损坏,引发停电、通信中断甚至更严重的安全事故。因此,在进行降水打井前,须采取一系列措施,确保作业过程安全、有序,有效避开地下电缆。

中空玻璃的用途及产品作用有什么呢,为什么生活中常会看到中空玻璃的存在。对流过程是玻璃两侧温度的差异,因此空气从冷侧脱落,在热侧上升,空气对流,构成能量损失,构成这种现象有很多原因

因此,联想企业科技集团针对中国相关企业单位对大容量、高密度的存储服务器的需求,沈阳联想服务器代理推出Lenovo ThinkServer DN8836,在4U机箱内提供36个大容量硬盘位,同时满足了运算和存储的要求,并实现了价格/存储空间比,是冷数据存储、视频监控、云存储、大数据和CDN应用的选择。

高压电缆的阻燃措施是确保电力系统安全、预防火灾和减少火灾损失的重要手段。在高压电缆的设计、生产和安装过程中,采取有效的阻燃措施,能够显著降低火灾发生的风险。以下是一些主要的阻燃措施:
珍珠棉和PP棉是两种常见的包装材料,它们在保护和缓冲物品方面有着广泛的应用。虽然它们在外观和手感上有些相似,但实际上它们具有不同的材料特性和用途。
polo衫的发展穿好的秘诀是什么 相信很多男士都polo衫,它是仅次于西装,深受众多男士喜爱的服装单品,穿的人多,但真正了解它的人却很少,

山药茯苓草本膏是一种结合了山药、茯苓以及其他中药材(如薏苡仁、芡实、莲子等)制作而成的草本膏体。利水消肿:山药茯苓草本膏能有效促进身体代谢,加快体内水分的排出,有助于缓解水肿症状。

白皮松苗木的种植方法可以按照以下步骤进行,确保清晰且详细地分点表示:1.种子处理采集:选择健康、生长良好的20~60年生的林木作为采种母树。当球果由绿变黄绿色时(9-10月),即可采种。